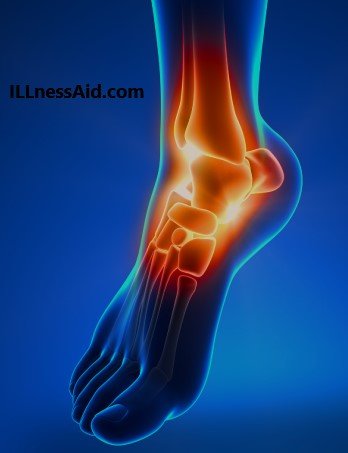
A high ankle sprain is an injury, In which high ankle ligaments are damaged and torn. These ligaments connect the tibia to the fibula and help to stabilize the area for activities like walking and running. They serve as a shock absorber, prevent the tibia and fibula from spreading too far apart. So, when you run, these ligaments experience high force and increase the chance of high ankle sprain also called a syndesmotic injury.
CAUSES OF HIGH ANKLE SPRAIN
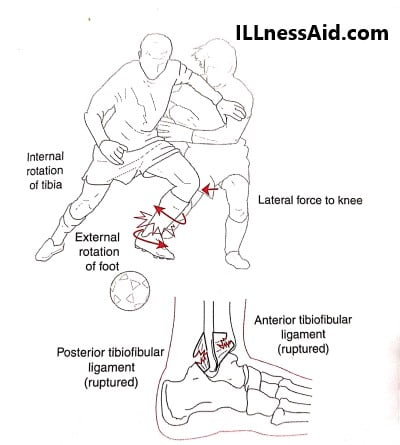
The most common mechanism for this sprain is the external rotation of the foot relative to the tibia. Other mechanisms are eversion of the talus within the ankle mortise and excessive dorsiflexion. This injury is more common in athletes who play football, basketball, baseball, etc because of more athletic activities.
Diagnostic Tests Of High Ankle Sprain
Patients with high ankle sprain usually complain of pain anteriorly between the distal tibia and fibular and posteromedially at the level of the ankle joint. The pain is worsen when pushing off the ground or bearing weight. Physical examination begins with palpation of the limb to identify the tenderness. There are also many tests to evaluate the high ankle sprain. These tests are:
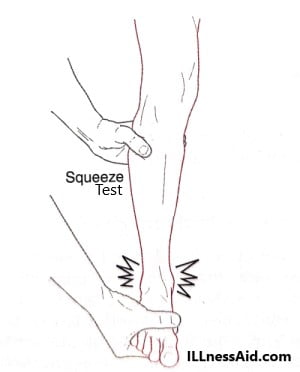
1. SQUEEZE TEST – This test is start with compression of the fibula to the tibia above the midpoint of the calf causing separation of the two bones distally. The test is said to be positive if it causes pain in the area of the syndesmosis( high ankle area).
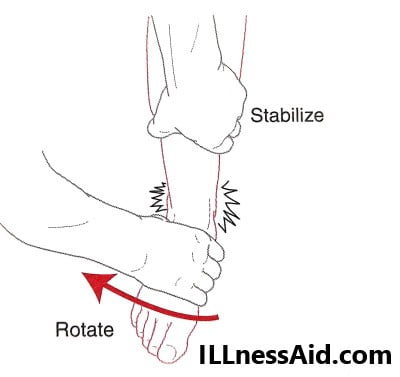
2. EXTERNAL ROTATION TEST– You will externally rotate the foot while the leg is stabilized with the knee flexed 90 degrees. The test will positive if the pain is elicited over the syndesmosis( high ankle area).
3. CROSSED LEG TEST – This is similar to the squeeze test, but it is self-administered. The patient sits with a mid tibia of the affected leg resting on the opposite knee and also applies a gentle downward force on the medial side of the knee. The test is positive if the pain is elicited at the area of the syndesmosis.
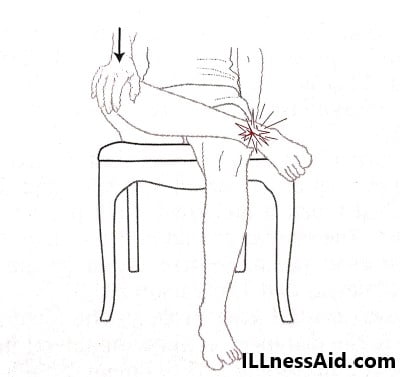
4. FIBULA TRANSLATION (DRAWER) TEST – For this test, translation of the fibula will start from anterior to posterior and increased translation compared to the opposite side. Pain with the maneuver will indicate a positive test result.
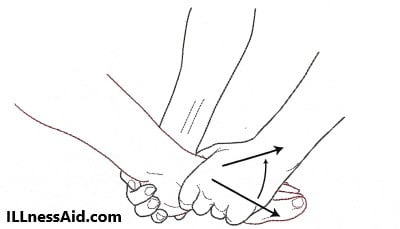
5. COTTON TEST – As you can see below the picture, the Translation of the talus within the mortise from medial to lateral and increased translation compared to the opposite side. Pain with the maneuver will indicate a high ankle sprain( Syndesmotic Injury).
Treatment Plan For High Ankle Sprain
For the initial treatment, we firstly classified the high ankle sprain on the basis of the extent of tearing of ligaments. Let’s see the below table to understand the classification:
| Grade | Injury | History | Examination |
| I | Stretch | 1. Subacute pain and swelling 2. Continued athletic activity | 1. Squeeze test 2. External rotation test 3. Stable ankle 4. Mild swelling |
| II | Partial tear | 1. Acute pain and swelling 2. Inability to continue an athletic activity | 1. Moderate swelling 2. Squeeze test 3. External rotation test |
| III | Complete tear | 1. Acute severe pain and swelling 2. Inability to walk | 1. Severe swelling 2. Squeeze test |
The initial treatment of grades I and II high ankle sprains usually is nonoperative and consists of a three-phase rehabilitation program. and for grades III, you should go to the doctor and talk to them about your problems. If you want to follow the below three-phase rehabilitation program be sure you are in grades I and II. Let’s discuss the treatment:
THREE PHASE TREATMENT PROGRAM
PHASE I
- You should control pain and swelling with rest, ice, compression, elevation; toe curls, ankle pumps, cryotherapy, etc.
- Do temporary stabilization( short leg cast, splint, brace, heel lift)
- Non-weightbearing with crutches
CRITERIA FOR PROGRESSION
- Pain and swelling subside
- You are able to partial weight bear with an assistive device
PHASE II
- You can partial weighbearing without pain in this phase, so do ambulation
- Do low-level balance training: bilateral standing activity; standing on a balance pad or several layers of towels
- Do lower-level strengthening with theraband
CRITERIA FOR PROGRESSION
- You are full ambulation with weight-bearing without pain, possibly with ankle brace or heel lift
PHASE III
- Unilateral balance training
- Progress from double-heel raises to single heel raises
- Treadmill walking or overground walking
- Progression to fast walking
CRITERIA FOR PROGRESSION
- Able to perform heel raises in unilateral stance
After this, there will be the last phase which we called phase IV but that is not a treatment phase. In this phase, the patient is recovered and is able to fast pain-free walking, focus on jogging to run progression, and do sport-specific training.
Follow the program is the key for your improvment
ILLnessAid
Thank you for reading this far, today we talk about high ankle sprains and treatment about it. If you have any doubt regarding this, you can comment below or go on the contact us page.

