Wrist drop is a medical condition in which a person experiences weakness or paralysis of the muscles responsible for wrist extension, resulting in the inability to lift the wrist and fingers upwards. It is often a sign of an underlying condition that affects the nerves or muscles responsible for controlling the wrist and hand.
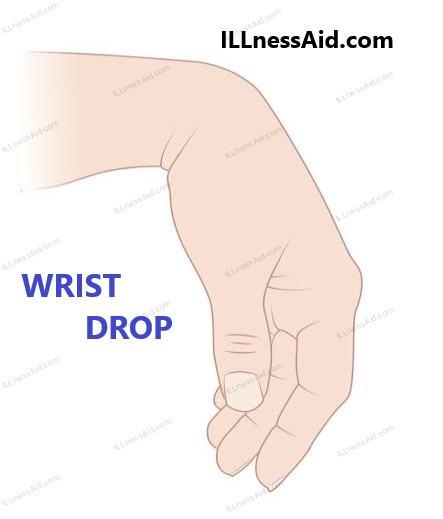
In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for wrist drop.
CAUSES
Wrist drop can be caused by various underlying medical conditions. Some of the most common causes of wrist drop include:
- Radial Nerve Injury: The radial nerve is responsible for controlling the muscles that extend the wrist and fingers. Any injury to the nerve can result in wrist drop. The injury can be caused by trauma, such as a direct blow to the arm, or by compression of the nerve.
- Brachial Plexus Injury: The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that run from the spine to the shoulder and arm. Any injury to this network of nerves can cause wrist drop.
- Stroke: A stroke can cause damage to the brain, which can affect the nerves that control the wrist and hand. Wrist drop is a common symptom of a stroke.
- Radiculopathy: Radiculopathy is a condition that affects the nerves that exit the spinal cord. It can cause weakness or paralysis in the muscles controlled by those nerves, including the wrist extensors.
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Guillain-Barre syndrome is a rare autoimmune disorder that can cause paralysis of the muscles. It can affect the nerves that control the wrist and hand, resulting in wrist drop.
SYMPTOMS OF WRIST DROP
The main symptom of wrist drop is the inability to lift the wrist and fingers upwards. Other symptoms may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the hand or arm
- Pain in the wrist, arm, or shoulder
- Weakness in the arm
- Difficulty gripping objects
In some cases, the symptoms may be temporary and resolve on their own. However, if the symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical attention.
TREATMENT FOR WRIST DROP
The treatment for wrist drop depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Some of the treatment options include:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected arm. A physical therapist may recommend exercises to strengthen the wrist and hand muscles and improve grip strength.
- Medication: If the wrist drop is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as Guillain-Barre syndrome, medication may be prescribed to treat the condition and alleviate the symptoms.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be required to repair the nerve or muscle damage that is causing the wrist drop. Surgery may also be used to decompress the nerve or remove any tumors that may be causing compression of the nerve.
- Wrist Splinting: A wrist splint can be worn to support the wrist and prevent it from bending. This can help to reduce the strain on the affected muscles and promote healing.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help to improve the ability to perform everyday tasks, such as dressing and grooming, using adaptive equipment, and modifying the environment to make it more accessible.
EXERCISES FOR WRIST DROP
There are several exercises that can help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the wrist and hand muscles affected by wrist drop. However, the specific exercises will depend on the underlying cause of the wrist drop, and it’s important to consult a physical therapist or healthcare provider to develop an appropriate exercise program. Here are some examples of exercises that may be recommended for wrist drop:
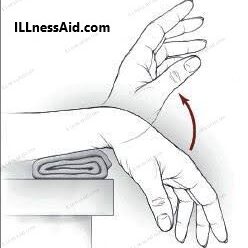
This exercise helps to strengthen the wrist extensors and flexors.
- Sit or stand with your arms at your sides.
- Bend your elbow to 90 degrees and rest your forearm on a table or armrest with your palm facing down.
- Slowly raise your hand and wrist up towards the ceiling, keeping your elbow and upper arm still.
- Hold the position for a few seconds, then slowly lower your hand and wrist back down.
- Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other arm.
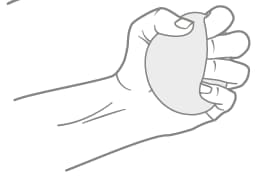
This exercise helps to improve grip strength and dexterity.
- Hold a soft ball or stress ball in the affected hand.
- Squeeze the ball as hard as you can, then release.
- Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.
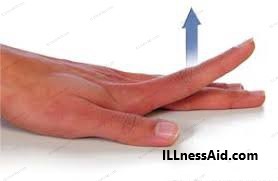
This exercise helps to improve the strength and flexibility of the finger muscles.
- Sit or stand with your arms at your sides.
- Place your affected hand on a flat surface with your palm facing down.
- Slowly lift each finger up one at a time, then lower it back down.
- Repeat for all fingers, then repeat the exercise with your palm facing up.
- Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.
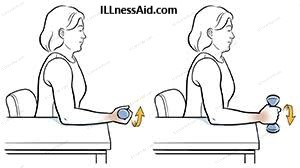
This exercise helps to improve the strength and flexibility of the wrist and forearm muscles.
- Sit or stand with your arms at your sides.
- Hold a small weight or a can of soup in your affected hand.
- Rest your forearm on a table or armrest with your elbow bent to 90 degrees and your palm facing down.
- Slowly rotate your forearm so that your palm faces up, then rotate back to the starting position.
- Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.
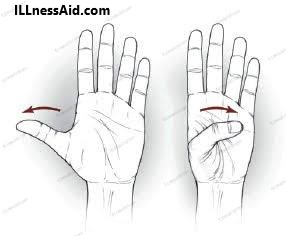
This exercise helps to improve the strength and flexibility of the thumb muscles.
- Sit or stand with your arms at your sides.
- Hold your affected hand in front of you with your palm facing up.
- Slowly move your thumb away from your fingers, then back towards them.
- Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.
It’s important to start with low resistance and gradually increase the intensity of the exercises as you progress. If you experience any pain or discomfort during the exercises, stop immediately and consult with your healthcare provider.
PREVENTION OF WRIST DROP
Wrist drop can be prevented by taking certain precautions such as:
- Avoiding Trauma: Avoid activities that may cause trauma to the arm, such as contact sports or heavy lifting. Use protective gear, such as elbow pads, when participating in sports that may cause trauma to the arm.
- Maintaining Good Posture: Poor posture can lead to compression of the nerves and blood vessels in the arm, which can increase the risk of developing wrist drop. Maintain good posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping to reduce the risk of nerve compression.
- Stretching Exercises: Regular stretching exercises can help to maintain flexibility in the wrist and hand muscles, which can help to reduce the risk of developing wrist drop.
- Ergonomic Workspace: Make sure your workspace is ergonomic and designed to reduce the strain on your wrists and arms. Use a comfortable chair, a keyboard, and a mouse that are positioned correctly, and take frequent breaks to stretch and move your arms.

CONCLUSION
Wrist drop is a condition that affects the ability to lift the wrist and fingers upwards, and it can due to a variety of underlying medical conditions. The symptoms of wrist drop include weakness, pain, and numbness in the wrist and hand. Treatment options for wrist drop depend on the underlying cause and may include physical therapy, medication, surgery, wrist splinting, and occupational therapy. By taking precautions to prevent wrist drop, such as avoiding trauma and maintaining good posture, you can reduce the risk of developing this condition. If you experience symptoms of wrist drop, it is important to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Thank you for reading this far, today we talk about wrist drop and his treatment, exercises, and more. If you have any doubts regarding this then go to the contact us page or comment below.

