Carpal boss syndrome, also known as carpal bossing, is a condition that affects the back of the hand at the base of the index or middle finger. It is characterized by the presence of a bony lump or protuberance, which can be painful and limit hand function. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, exercises of carpal boss syndrome.
CAUSES OF CARPAL BOSS SYNDROME
The exact cause of carpal boss syndrome is unknown, but it is believed to be a result of repetitive hand movements or trauma. The condition can also be associated with arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, which is a degenerative joint disease that causes the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. To know more: Osteoarthrosis: Causes, Features, & PT Management.
Repetitive hand movements, such as typing, playing musical instruments, or using hand tools, can cause strain on the hand and wrist, leading to the development of carpal boss syndrome. Trauma to the hand, such as a fracture or dislocation, can also cause the condition. In some cases, carpal boss syndrome can occur without any apparent cause.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
The main symptom of carpal boss syndrome is the presence of a bony lump on the back of the hand at the base of the index or middle finger. The lump can be small or large and is usually hard and immovable. It may be tender to the touch and can cause pain and discomfort, particularly when pressure is applied to the area.
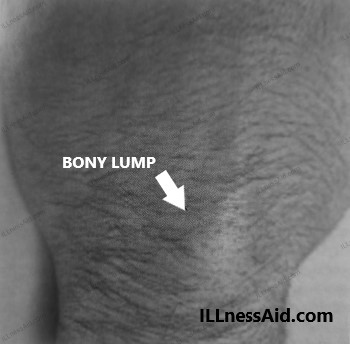
In addition to the bony lump, other symptoms of carpal boss syndrome can include:
- Swelling and inflammation in the affected area
- Limited range of motion in the affected finger
- Stiffness and soreness in the wrist and hand
- Weakness in the hand and fingers
- Numbness and tingling in the fingers
DIAGNOSIS
To diagnose carpal boss syndrome, a doctor will perform a physical examination of the hand and wrist. The doctor will look for the presence of a bony lump on the back of the hand and may perform a range of motion tests to assess hand and finger function. X-rays may also be taken to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions, such as a bone tumor or ganglion cyst.
TREATMENT OF CARPAL BOSS SYNDROME
The treatment of carpal boss syndrome depends on the severity of the condition and the level of pain and discomfort experienced by the patient. In mild cases, rest and self-care measures may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms. This may include:
- Avoiding repetitive hand movements that exacerbate symptoms
- Applying ice to the affected area to reduce swelling and inflammation
- Taking over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to relieve pain and discomfort
In more severe cases, additional treatment may be necessary. This can include:
- Wearing a splint or brace to immobilize the hand and wrist and prevent further damage
- Physical therapy to strengthen the hand and wrist and improve range of motion
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain
- Surgery to remove the bony lump and restore hand function
Surgery is usually only recommended in cases where non-surgical treatments have been unsuccessful or if the bony lump is causing severe pain and limiting hand function. The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia and involves making an incision over the bony lump and removing it. The incision is then closed with sutures or staples, and a splint or cast is applied to the hand and wrist to aid in healing.
Recovery from surgery can take several weeks, and physical therapy may be necessary to regain full hand function. In some cases, the bony lump may recur after surgery, particularly if the underlying cause of the condition is not addressed.
EXERCISES FOR CARPAL BOSS SYNDROME
Before beginning any exercises for carpal boss syndrome, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to determine the appropriate exercises for your individual needs and level of severity. Depending on the severity of your condition, some exercises may be contraindicated or require modification.
That being said, here are a few exercises that may be beneficial for individuals with carpal boss syndrome:
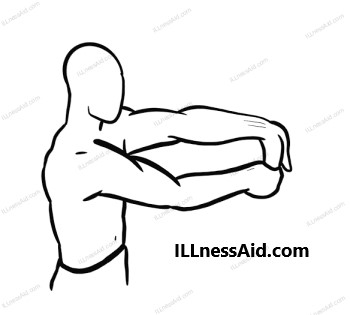
- To perform this stretch, extend your arm in front of you with your palm facing down. Use your other hand to gently pull your fingers back towards your wrist until you feel a stretch in your forearm. Hold the stretch for 10-15 seconds, then release. Repeat on the other side.
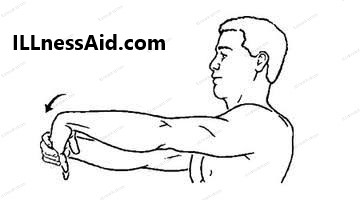
- To perform this stretch, extend your arm in front of you with your palm facing up. Use your other hand to gently press down on the back of your hand until you feel a stretch in your forearm. Hold the stretch for 10-15 seconds, then release. Repeat on the other side.
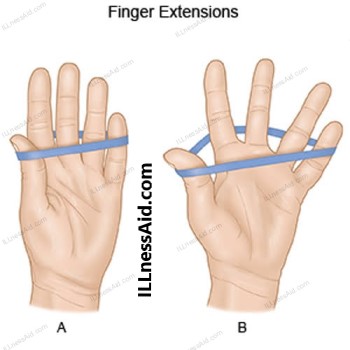
- To perform this exercise, place a rubber band around all five fingers and the thumb of one hand. Spread your fingers apart to stretch the rubber band, then release. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.
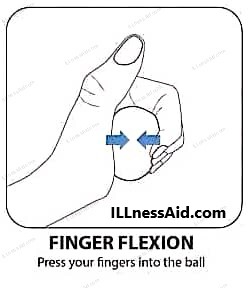
- To perform this exercise, place a ball around all five fingers and the thumb of one hand. Bring your fingers towards your palm to press the ball, then release. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.


- To perform this exercise, hold a softball or rolled-up towel in your hand and squeeze it as hard as you can without causing pain. Hold the squeeze for 5-10 seconds, then release. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions, then switch to the other hand.
These exercises can help improve the range of motion, reduce stiffness and soreness, and strengthen the muscles of the hand and wrist. However, it is important to start with low resistance and gradually increase as your strength improves. If you experience pain or discomfort during any of these exercises, stop immediately and consult with your healthcare provider.
PREVENTION
Preventing carpal boss syndrome can be challenging, particularly if the condition is caused by repetitive hand movements. However, there are some steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition or prevent it from worsening. These include:
- Taking frequent breaks when performing repetitive hand movements to give the hands and wrists a chance to rest
- Using ergonomic equipment, such as a keyboard or mouse, that is designed to reduce strain on the hands and wrists
- Maintaining good posture when sitting or standing to reduce strain on the upper body
- Wearing protective gear when participating in activities that can cause trauma to the hands, such as sports or manual labor
It is also important to seek medical attention if symptoms of carpal boss syndrome develop. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve the chances of successful treatment.
CONCLUSION
Carpal boss syndrome is a condition that affects the back of the hand at the base of the index or middle finger. It is characterized by the presence of a bony lump, which can cause pain and limit hand function. The condition is often caused by repetitive hand movements or trauma and can be associated with arthritis. Treatment options include rest, splinting, physical therapy, and surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Prevention measures, such as taking frequent breaks and using ergonomic equipment, can help reduce the risk of developing the condition or prevent it from worsening. If symptoms of carpal boss syndrome develop, seeking medical attention early can improve the chances of successful treatment and prevent further damage to the hand and wrist.
Thank you for regarding this far, If you have any doubts regarding this then you can go to the contact us page or comment below.


Pingback: Osteoarthrosis: Causes, Features, & PT Management. - physiociti