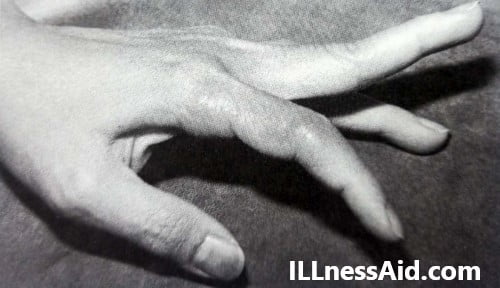
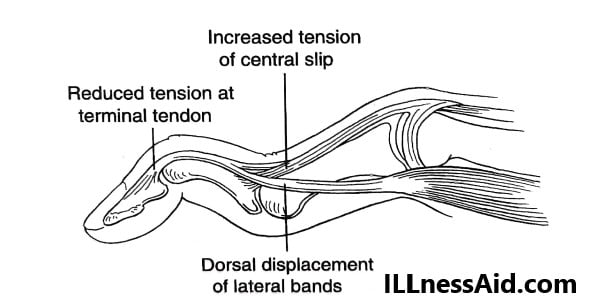
A deformity in which the Proximal Interphalangeal joint is hyperextended and the Distal Interphalangeal joint is flexed is known as Swan Neck Deformity. It occurs through Intrinsic, Extrinsic, and articular abnormal factors. In this deformity, The Proximal interphalangeal(PIP) joint decreases function due to loss of flexibility. The lateral bands become tight and dorsally displaced to extend the DIP joint which is reduced(shown in the figure).
CAUSES
There are many etiology factors for swan neck deformity including:
- Rheumatologic disease
- Extensor terminal tendon injuries
- Spastic conditions
- Injuries that cause volar plate laxity
- Generalized ligamentous laxity
- Fractures to the middle phalanx(that heal in hyperextension)
- Can occur secondary to surgical procedures like flexor digitorum profundus graft where flexor digitorum superficialis is absent
CLASSIFICATION OF SWAN NECK DEFORMITY
The classification of deformity helps to determine the treatment method. There are four classifications as follows:
- TYPE I: PIP joint is flexed in all position
- TYPE II: PIP flexion is limited by tightness(intrinsic)
- TYPE III: PIP flexion is limited by articular factors in all positions(remain good radiographically)
- TYPE IV: PIP flexion is limited in all positions as noted radiographically
TREATMENT FOR SWAN NECK DEFORMITY
Treatment of the deformity depends on the etiology factor of the PIP joint and its related anatomic structures. The Treatment can be surgical with post-operative or non-operative. now let’s discuss treatment methods one by one.
SURGICAL WITH POST-OPERATIVE TREATMENT
Operative treatment is used to prevent hyperextension posture of the PIP joint following the flexion of the DIP joint. Surgical correction obtains by tendon transfers for active dynamic restoration of this balance. It is done by tendon grafts. Now “after the surgical procedure post-operative treatment” are followed:
A. GOALS OF POSTOPERATIVE TREATMENT
- Boost wound healing
- Control edema
- Scar management
- Prevent any rupture
- Limit PIP extension and promote full DIP extension
- Maintain range of motion of uninvolved digits
- Promote full flexion(active)
B. INDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS FOR POSTOPERATIVE
INDICATIONS
- Always follow after surgical procedures to relieve the deformity.
PRECAUTIONS
- Do not excessive exercise
- In procedures that involve joint fusions, do not use them
- Always know what type of surgical procedure happen
C. HOW IT IS DONE(POST-OPERATIVE THERAPY)?
1. GENERAL CARE(FIRST STEPS)
- Should see the condition of surgical sites
- Then control the edema
- Wound care is follow up
- Scar and pain management should take the account
- Maintain ROM of the uninvolved joints(digits)
- At last Manage the ADL(activities of daily living)
2. WEEKS 1 TO 4
- Use the splint to limit the active flexion and extension
- Should start passive flexion of PIP and MCP joint
3. WEEK 6
- Should start passive exercises(flexion and extension) for all joints
- Start grip strength exercises
D. COMPLICATION OF SURGICAL TREATMENT
- Infection
- Excessive edema
- Limit ROM
- Scarring
- Rupture of tenodesis
NON-OPERATIVE TREATMENT
A. GOALS OF NON-OPERATIVE
- Encourage a balance of the extensor mechanism
- Increase joint range of motion
- Maintain range of motion of uninvolved digits and wrist
- Decrease intrinsic tightness
B. INDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS FOR NON-OPERATIVE
INDICATIONS
- Supple deformities are the indication of this.
PRECAUTIONS
- Dynamic imbalance should check
- Volar plate laxity
- Intrinsic muscle tightness
C. HOW IT IS DONE(NON-OPERATIVE THERAPY)?
- Start with active and passive range of motion exercises
- Do the stretching of intrinsic muscles
- Use the splint to balance the finger extension. A tripoint splint should use to prevent PIP hyperextension and restores DIP extension.
D. COMPLICATION OF NON-OPERATIVE TREATMENT
- Continuation of deformity
- The reducible deformity can become the fix
- Hand function reduce
PREVENTION IS THE KEY OF HEALTHY LIFE
ILLnessAid
Thank you for reading this far, today we talk about swan neck deformity and its treatment. this content is for your knowledge only u should contact a doctor or therapist before applying treatment. If you have any doubts regarding this then u can contact us.

