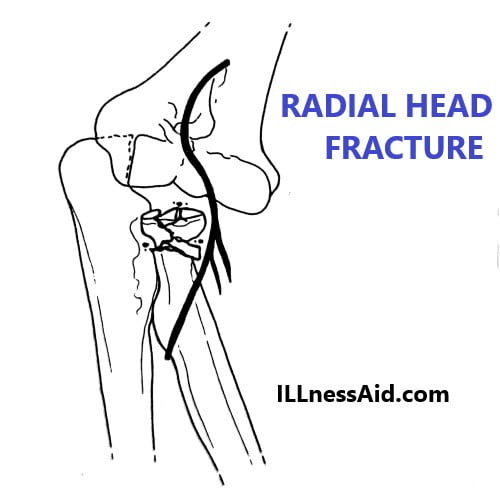
Radial head fracture is a common injury in adults and rare in children. But if we see radial neck fracture, That is common in children. The mechanism of this fracture are:
- A fall on an outstretched hand with valgus force means indirect trauma
- Direct trauma on the elbow, usually a blow on the lateral side(elbow)
CLINICAL FEATURES OF RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE
Patients with radial head fracture shows:
- Pain on the lateral side(elbow)
- Minimal swelling
- Restriction of elbow movement and supination of the forearm
- Tenderness on radial head
- Crepitus can present
EXAMINATION OF RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE
DIAGNOSTIC FACTS
If a patient has a radial head fracture and we want to examine that patient then we should see first these two points:
- Tenderness on radial head present
- Painful forearm rotation and movement of the elbow also
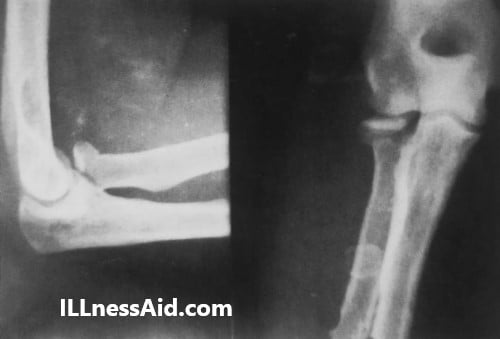
Now we should examine radiographically. A fracture case is always confirmed by radiography to see the severity.
RADIOGRAPH
Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the elbow help to see the case of a fracture means anatomy and displacements. Additional oblique radiographs describe the fracture line better.
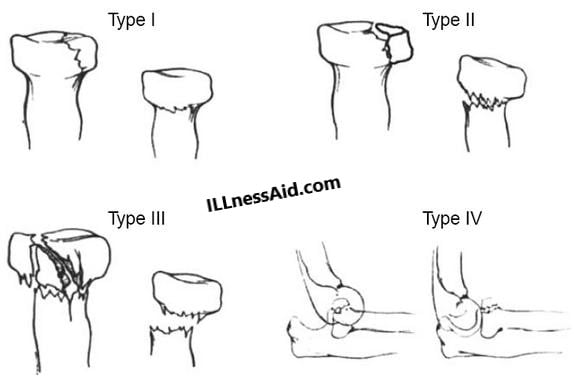
CLASSIFICATION OF RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE
Radial head fracture is classified by mason’s that is called Mason’s classification. Mason’s classification is also widely accepted. The classification of the fracture also helps in treatment. So let’s discuss mason’s classification of fracture(radius head) before we talk about treatment.
Mason classifies this fracture into 4 types:
- TYPE I: Nondisplaced fracture
- TYPE II: Small (marginal) fracture with depression, displacement, or angulation
- TYPE III: Comminuted fracture of the entire radial head or completely displaced fracture
- TYPE IV: Any type I, II, or III patterns associated with dislocation
TREATMENT OF RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE
Early we talk about the classification of radial head fracture and that we help us to determine the treatment. let’s talk about treatment according to classification:
NONDISPLACED TYPE I TREATMENT
- This type of fracture requires no immobilization or little immobilization.
- Active and passive range of motion can start after injury to promote a full range of motion
- Usually, within the first week, there should conditioning in the form of the elbow(flexion and extension), supination and pronation isometrics, and wrist and shoulder isotonic implementation.
- Stress will minimize on the radial head
- 3 to 6 weeks of active elbow movements can use along with wrist isotonic
TYPE II AND TYPE III TREATMENT
- In these fractures, we usually require open reduction and internal fixation(ORIF)
- Immobilization requires a certain time
- After immobilization, active and passive range of motion exercises should start
TYPE IV TREATMENT
- It requires frequently stabilization of the elbow
- Also, need excision of fragments
- This fracture cause some functional limitation so remember this
| TYPE | TREATMENT |
| TYPE I | Little or no immobilization, and early motion |
| TYPE II | Open reduction and internal fixation, and early motion |
| TYPE III | Open reduction and internal fixation, and early motion if possible |
| TYPE IV | Radial head resection, and guarded prognosis for return |
REHABILITATION PROTOCOL AFTER ORIF
IMMEDIATE MOTION PHASE(PHASE I)
GOALS
- Decrease inflammation and pain
- Regain full range of motion
- Prevent muscular atrophy
WEEK I
- Regain elbow active range of motion and active-assisted range of motion
- Start gripping exercises
- Begin isometric exercises of the elbow and wrist
- Start isotonic exercises for the wrist
INTERMEDIATE PHASE(PHASE 2)
GOALS
- Keep full elbow range of motion
- Continue elbow strengthening exercises
- Slowly increase functional demands
WEEK 3
- Start shoulder strengthening exercises and concentrate rotator cuff muscles
- Go on the range of motion exercises for elbow
- Begin light resistance elbow movement(flexion and extension)
- Start active assisted range of motion and passive range of motion supination and pronation to tolerance
WEEK 6
- Continue active assistive range of motion and passive range of motion supination and pronation to full range of motion
- Update shoulder program
- Go forward with elbow strengthening exercises
ADVANCED STRENGTHENING PHASE(PHASE 3)
GOALS
- Continue full elbow range of motion
- Increase power, strength, and endurance
- Slowly start sporting activities
WEEK 7
- Continue active-assistive range of motion and passive range of motion to full supination and pronation
- Start eccentric elbow movement(flexion and extension) with some support
- Start a plyometric exercise program
- Go on with the isotonic program for wrist, shoulder, and forearm
- Carry on this until 12 weeks
KEEP FOCUS ON REHABILITATION PROGRAM, IT IS IMPORTANT FOR YOUR LIFE AHEAD
ILLnessAid
Thank you for reading this far, today we talk about radial head fracture and its treatment, rehabilitation, and more. If you have any doubts regarding this you can comment below or go on the contact us page.

